本文共 12421 字,大约阅读时间需要 41 分钟。
PyTorch学习笔记01: PyTorch基本概念
张量的简介和创建
张量的概念
Tensor与Variable的关系:
-
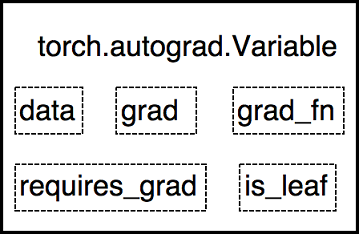
torch.autograd.Variable封装了Tensor,用于进行自动求导,其属性如下:data: 被包装的Tensorgrad:data的梯度grad_fn: 创建Tensor的Function,是自动求导的关键requires_grad: 指示是否需要梯度is_leaf: 指示是否是叶子结点
-
从PyTorch0.4.0版开始,
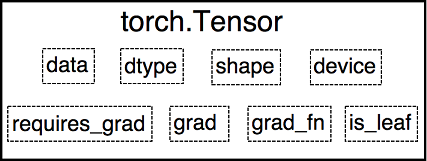
Variable并入Tensor,Tensor除Variable原有的属性以外,还有额外的三个属性:dtype: 张量的数据类型,如torch.FloatTensor,torch.cuda.FloatTensorshape: 张量的形状,如(64,3,224,224)device: 张量所在设备,'cpu'或'cuda'
张量的创建
有三类创建张量的方式: 直接创建, 依数值创建,依概率创建
| 创建方式 | API |
|---|---|
| 直接创建 | torch.tensor()torch.from_numpy(ndarray) |
| 依数值创建 | torch.zeros()torch.zeros_like()torch.ones() torch.ones_like()torch.full()torch.full_like()torch.arange()torch.linspace()torch.logspace()torch.eye() |
| 依概率创建 | torch.normal()torch.randn()torch.randn_like()torch.rand()torch.rand_like()torch.randint()torch.randint_like()torch.bernoulli()torch.randperm() |
直接创建张量
-
torch.tensor()torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)
从data创建tensor,参数意义如下:
data: 数据,可以是list或NumPy数组dtype: 数据类型,默认与data的一致device: 所在设备,'cpu'或'cuda'requires_grad是否需要梯度pin_memory是否存于锁页内存
-
torch.from_numpy(ndarray)从NumPy数组创建
Tensor.值得注意的是: 从torch.from_numpy创建的Tensor与原ndarray共享内存,当修改其中一个的数据时,另一个也将会被改动.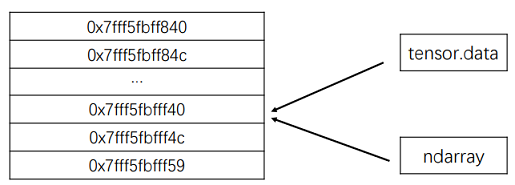
依数值创建张量
-
torch.zeros()torch.zeros(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
依size创建全0张量,参数意义如下:
size: 张量的形状,如(3,3),(3,224,224)out: 输出的张量layout: 内存中布局形式,有torch.strided,torch.sparse_coo等
-
torch.zeros_like()torch.zeros_like(input, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, requires_grad=False)
依
input形状创建全0张量 -
torch.ones(),torch.ones_like(): 类似于torch.zeros()和torch.zeros_like() -
torch.full(),torch.full_like():torch.full(size, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
依
input或size形状创建指定数据的张量size: 张量的形状,如(3,3)fill_value: 张量的值
-
torch.arange()torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
创建1维等差数列张量,数值区间为
[start,end)左闭右开区间start: 数列起始值end: 数列结束值step: 数列公差,默认为1
-
torch.linspace()torch.linspace(start, end, steps=100, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
创建均分的1维张量,数值区间为
[start,end]左闭右闭区间start: 数列起始值end: 数列结束值steps: 数列长度
-
torch.logspace()torch.logspace(start, end, steps=100, base=10.0, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
创建对数均分的1维张量,数值区间为
[start,end]左闭右闭区间start: 数列起始值end: 数列结束值steps:数列长度base:对数函数的底,默认为10
-
torch.eye()torch.eye(n, m=None, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
创建单位对角矩阵,默认为方阵
n: 矩阵行数m: 矩阵列数
依概率创建
-
torch.normal()torch.normal(mean, std, out=None)torch.normal(mean, std, size, out=None)
依正态分布生成矩阵
-
torch.randn(),torch.randn_like()torch.randn(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
依标准正态分布生成矩阵
-
torch.rand(),torch.rand_like(): 依均匀分布生成矩阵 -
torch.randint(),torch.randint_like(): 依区间[low, high)内的整数均匀分布生成矩阵 -
torch.bernoulli()torch.bernoulli(input, *, generator=None, out=None)
以
input为概率的伯努利分布生成矩阵 -
torch.randperm()torch.randperm(n, out=None, dtype=torch.int64, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
生成从
0到n-1的随机排列
张量的操作
张量的形态变换
| 形态变换 | API |
|---|---|
| 拼接与切分 | torch.cat()torch.stack()torch.chunk()torch.split() |
| 张量索引 | torch.index_select()torch.masked_select() |
| 形状变换 | torch.reshape()torch.transpose()torch.t()torch.squeeze()torch.unsqueeze() |
拼接与切分
-
torch.cat()torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
将张量按维度
dim进行拼接tensors: 张量序列dim: 要拼接的维度
-
torch.stack()torch.stack(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
将张量在新创建的维度
dim上进行拼接tensors: 张量序列dim: 要拼接的维度
torch.cat()和torch.stack()分别在现有维度上和新维度上拼接
t = torch.rand((2, 3))t_cat = torch.cat([t, t, t, t], dim=1)t_cat.shape # torch.Size([2, 12])t_stack = torch.stack([t, t, t, t], dim=1)t_stack.shape # torch.Size([2, 4, 3])
-
torch.chunk()torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
将张量按维度
dim进行平均切分,返回张量列表.若不能整除,最后一份张量将小于其它张量input: 要切分的张量chunks: 要切分的份数dim: 要切分的维度
a = torch.rand((2, 7)) list_of_tensors = torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=3) for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors): print("第{}个张量的形状是 {}".format(idx+1, t.shape)) # 第1个张量的形状是 torch.Size([2, 3])# 第2个张量的形状是 torch.Size([2, 3])# 第3个张量的形状是 torch.Size([2, 1]) -
torch.split()torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
将张量按维度
dim进行切分tensor: 要切分的张量split_size_or_sections: 为int时,表示每一份的长度;为list时,按list元素切分dim: 要切分的维度
张量索引
-
torch.index_select()torch.index_select(input, dim, index, out=None)
在维度
dim上,按index索引数据,并返回索引结果拼接的张量input: 要索引的张量dim: 要索引的维度index: 要索引数据的序号,数据类型必须为torch.long
t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3))idx = torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.long) # 索引的数据类型必须为torch.longt_select = torch.index_select(t, dim=0, index=idx)# t = tensor([[3, 6, 2],# [0, 1, 2],# [0, 1, 2]])# t_select = tensor([[3, 6, 2],# [0, 1, 2]])
-
torch.masked_select()torch.masked_select(input, mask, out=None)
按
mask中的True进行索引,不论input形状是什么样的,均返回一维张量input: 要索引的张量mask: 与input同形状的布尔类型张量
形状变换
-
torch.reshape()torch.reshape(input, shape)
变换张量形状,值得注意的是: 当张量在内存中连续时,新张量与input共享数据内存.
-
torch.transpose()torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1)
交换张量的两个维度
input: 要变换的张量dim0: 要交换的维度dim1: 要交换的维度
-
torch.t(): 两维张量转置,对矩阵而言,等价于torch.transpose(input, 0, 1) -
torch.squeeze()torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)
压缩长度为1的维度(轴)
dim: 若为None则移除所有长度为1的轴;若指定维度则当且仅当该轴长度为1时才可以被移除.
-
torch.unsqueeze()torch.usqueeze(input, dim, out=None)
依据
dim扩展维度
张量的数学运算
| 运算类型 | API |
|---|---|
| 加减乘除 | torch.add()torch.addcdiv()torch.addcmul()torch.sub()torch.div()torch.mul() |
| 指对幂 | torch.log(input, out=None)torch.log10(input, out=None)torch.log2(input, out=None)torch.exp(input, out=None)torch.pow() |
| 三角函数 | torch.abs(input, out=None)torch.acos(input, out=None)torch.cosh(input, out=None)torch.cos(input, out=None)torch.asin(input, out=None)torch.atan(input, out=None)torch.atan2(input, other, out=None) |
-
torch.add()torch.add(input, alpha=1, other, out=None)
逐元素计算
input + alpha × other \text{input} + \text{alpha} \times \text{other} input+alpha×other
-
torch.addcdiv(),torch.addcmul()torch.addcmul(input, value=1, tensor1, tensor2, out=None)
分别逐元素计算
input + value × tensor1 tensor2 input + value × tensor1 × tensor2 \text{input} + \text{value} \times \frac{\text{tensor1}}{\text{tensor2}} \\ \text{input} + \text{value} \times \text{tensor1} \times \text{tensor2} input+value×tensor2tensor1input+value×tensor1×tensor2
计算图与autograde
计算图
计算图的构建和反向传播
计算图是用来描述运算的有向无环图.计算图有两个主要元素: 结点(Node)和边(Edge)
- 结点表示数据,如向量,矩阵,张量
- 边表示运算,如加减乘除卷积等
下图为运算 y = ( x + w ) × ( w + 1 ) y = (x+ w) \times (w+1) y=(x+w)×(w+1)的计算图:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dc8IqIcI-1595936653671)(image-20200728174954681.png)]
使用PyTorch框架构建上述计算图的代码如下:
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)a = torch.add(w, x) b = torch.add(w, 1)y = torch.mul(a, b)
各节点的grad_fn属性记录创建该节点的方法,用于反向传播:
print("w.grad_fn", w.grad_fn) # w.grad_fn Noneprint("x.grad_fn", x.grad_fn) # x.grad_fn Noneprint("a.grad_fn", a.grad_fn) # a.grad_fn print("b.grad_fn", b.grad_fn) # b.grad_fn print("y.grad_fn", y.grad_fn) # y.grad_fn 调用张量y的backward()方法即可进行反向传播,调用节点的grad属性可以查看其梯度
y.backward()print(w.grad) # tensor([5.])
叶子节点
不依赖于其他节点的节点被称为叶子节点,张量的is_leaf属性指示张量是否为叶子节点.
print("w.is_leaf:", w.is_leaf) # w.is_leaf: Trueprint("x.is_leaf:", x.is_leaf) # x.is_leaf: Trueprint("a.is_leaf:", a.is_leaf) # a.is_leaf: Falseprint("b.is_leaf:", b.is_leaf) # b.is_leaf: Falseprint("y.is_leaf:", y.is_leaf) # y.is_leaf: False 为节省内存开销,在反向传播结束之后,非叶子节点的梯度会被释放掉:
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)a = torch.add(w, x) b = torch.add(w, 1)y = torch.mul(a, b)y.backward()print(w.grad)print("w.grad:", w.grad) # w.grad: tensor([5.])print("x.grad:", x.grad) # x.grad: tensor([2.])print("a.grad:", a.grad) # a.grad: Noneprint("b.grad:", b.grad) # b.grad: Noneprint("y.grad:", y.grad) # y.grad: None 在执行反向传播以前,调用非叶子节点的retain_grad()方法就可以在反向传播结束之后仍保留该节点的梯度
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)a = torch.add(w, x) b = torch.add(w, 1)y = torch.mul(a, b)a.retain_grad()y.retain_grad()y.backward()print("w.grad:", w.grad) # w.grad: tensor([5.])print("x.grad:", x.grad) # x.grad: tensor([2.])print("a.grad:", a.grad) # a.grad: Noneprint("b.grad:", b.grad) # b.grad: tensor([2.])print("y.grad:", y.grad) # y.grad: tensor([1.]) autograde自动求导
torch.autograd包下有两个用于自动求导的API,分别对所有节点求梯度和对指定节点求梯度.
-
torch.autograd.backward(): 用于对计算图中所有节点求取梯度torch.autograd.backward(tensors, grad_tensors=None, retain_graph=None, create_graph=False)
该方法用于对计算图中所有节点求取梯度,每个节点的梯度会累加进该节点的
grad属性中tensors: 用于求导的张量,如lossretain_graph: 保存计算图,以便多次重复对该计算图求导create_graph: 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导grad_tensors:多个梯度的权重
经过断点调试可以证明,当我们调用计算图中张量的
backward()方法时,本质上是在调用``torch.autograd.backward()`方法.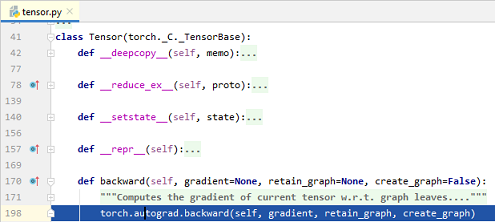
-
torch.autograd.grad(): 用于求取对指定节点的梯度torch.autograd.grad(outputs, inputs, grad_outputs=None, retain_graph=None, create_graph=False)
该方法用于求取计算图中指定节点的梯度,梯度值会直接返回,不会累加进
grad属性中outputs: 用于求导的张量,如lossinputs: 需要梯度的张量create_graph: 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导retain_graph: 保存计算图,以便多次重复对该计算图求导grad_outputs: 多个梯度的权重
通过正确设置上述API的retain_graph参数,可以实现多次重复对计算图反向传播运算.
# 未设置retain_graph参数时,重复反向传播报错w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)a = torch.add(w, x)b = torch.add(w, 1)y = torch.mul(a, b)y.backward()y.backward() # RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time, but the buffers have already been freed.
# 未设置retain_graph参数时,重复反向传播报错w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)a = torch.add(w, x)b = torch.add(w, 1)y = torch.mul(a, b)y.backward(retain_graph=True)y.backward() print(w.grad) # tensor([10.]), 两次重复反向传播,梯度累加5*2=10
通过正确设置上述计算图的create_graph参数,可以实现高阶求导
x = torch.tensor([3.], requires_grad=True)y = torch.pow(x, 2)grad_1 = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, create_graph=True) # 计算y对x的一阶导数grad_1,并将grad_1加入计算图print(grad_1) # (tensor([6.], grad_fn=),) grad_1在计算图中,因此存在反向传播函数grad_2 = torch.autograd.grad(grad_1[0], x) # 计算y对x的二阶导数grad_2print(grad_2) # (tensor([2.]),)
使用自动求导时要注意的问题
-
梯度不会自动清零,因此在记得在合适的时候将梯度手动清零.
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)for i in range(4): a = torch.add(w, x) b = torch.add(w, 1) y = torch.mul(a, b) y.backward() print(w.grad) w.grad.zero_() # 进入下次循环前将梯度清零
-
依赖于叶子节点的节点,其
requires_grad属性默认为True. -
参与反向传播的节点应尽量避免in-place操作.
在PyTorch中,in-place操作的函数通常以下划线
_结尾.-
对于叶子节点,进行in-place操作时会报错.
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)y = torch.add(w, x)w.add_(1) # 或 w+=1# 报错: RuntimeError: a leaf Variable that requires grad is being used in an in-place operation.
-
即使是非叶子节点,如果在构建好计算图后再进行in-place操作,在反向传播时,仍然会报错.
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)a = torch.add(w, x)b = torch.add(w, 1)y = torch.mul(a, b)a.add_(1) # 在进行反向传播前,对节点进行了in-place操作y.backward() # 报错: one of the variables needed for gradient computation has been modified by an inplace operation
究其原因,PyTorch框架使用
Tensor对象的_version属性来记录版本,每进行一次in-place操作,_version属性加1,若在前向传播和反向传播中某节点的_version属性不匹配,则就会报错.
-
转载地址:http://rwhlz.baihongyu.com/